Korea Culture and Arts Foundation (now Art Council Korea, ARKO for short), Korea TV Collection
Culture and Arts Promotion Act
* Source: Multilingual Glossary of Korean Art by Korea Arts Management Service
Related
-

Grand Craft Exhibition of Korea
The Grand Craft Exhibition of Korea is a competition organized by the Korean Fine Arts Association [Mihyeop] and invites entries for crafts in each category. With the abolition of the government-sponsored National Art Exhibition (Gukjeon) in 1949 right after the establishment of the government of the Republic of Korea, its crafts section was temporarily included in the Grand Art Exhibition of Korea hosted by the Korean Fine Arts Association from 1982 but began to be operated separately from 1986. The first competition was held in 1986 and organized by the MMCA. From the second edition (1987) through the thirteenth edition (1998), it was operated by the Korean Fine Arts Association. With the eighteenth edition in 1999, the crafts section was officially included in the Grand Art Exhibition of Korea. At the time, the Operating Committee for the Grand Craft Exhibition of Korea was established, and the Korea Culture and Arts Foundation began sponsoring the competition. The fields of the competition were divided into metal, ceramics, wood-lacquering, dyeing, and others, and centered on established artists. The Grand Craft Exhibition of Korea is responsible for evaluating the workmanship and artistry of professional artists in each craft field.
-

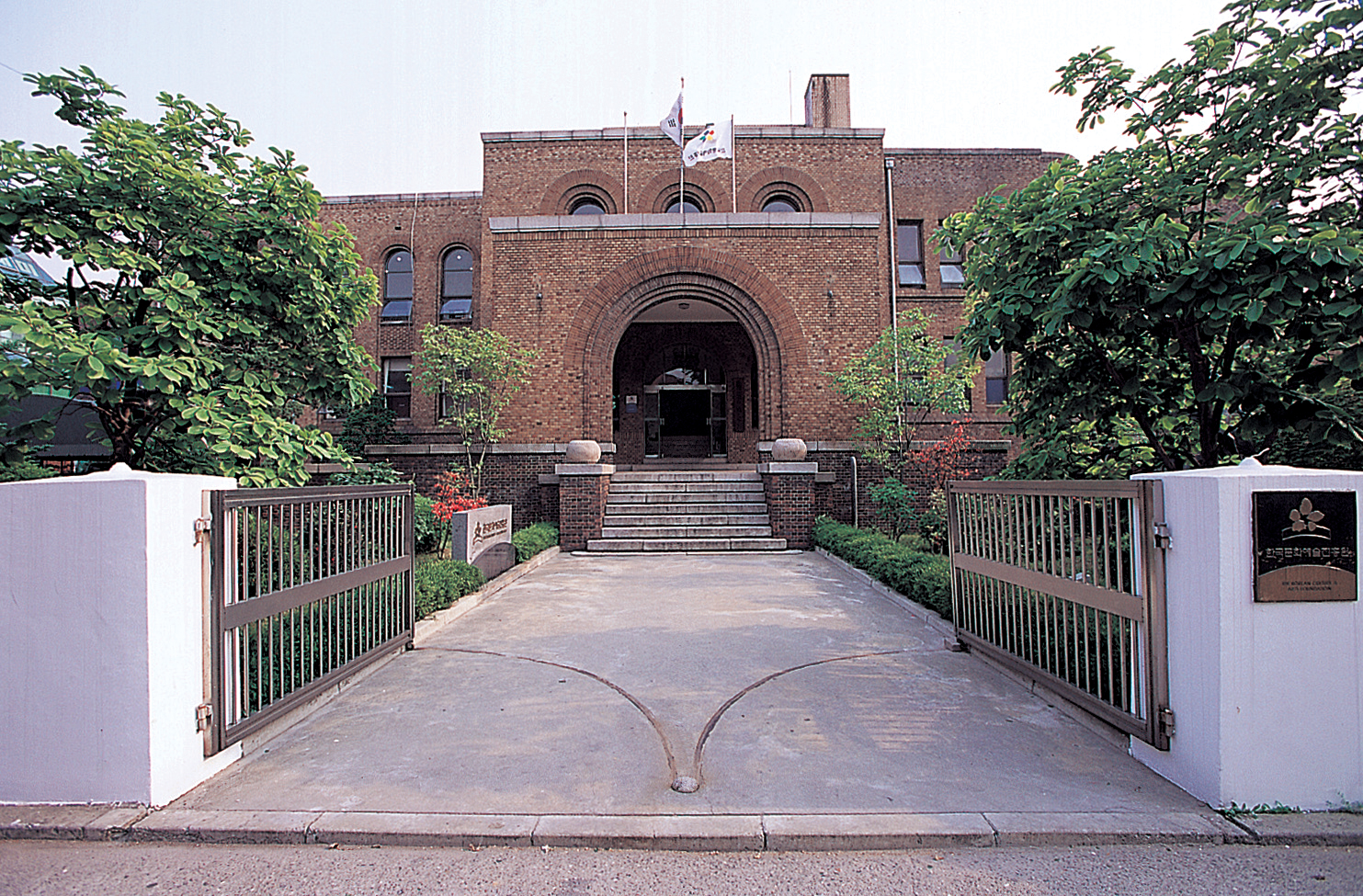
Arts Council Korea (ARKO)
Arts Council Korea (ARKO) is a cultural and artistic policy review organization established under the Prime Minister's Office based on the 1973 Culture and Arts Promotion Act. It was abolished in 2000 following revision of the law. In the beginning, the Arts Council Korea was established to contribute to the development of national culture by continuing traditional cultural arts and creating new creative expressions by supporting projects and activities for the promotion of culture and arts. The council played a role in planning basic policies and plans for the promotion of culture and arts, deliberation on matters concerning the creation and operation of the Culture and Arts Promotion Fund, and deliberation on other important matters concerning the promotion of culture and arts. The council consisted of less than 17 members, including one chairperson (the Prime Minister) and one vice-chairperson (the Minister of Culture and Public Information) (1979. 3. 28. Revised). In addition, expert members could be appointed to collect, survey, research, and attend meetings of the council on the promotion of culture and arts. Also, local culture and arts promotion committees could be established in each city and province (1983. 4. 25. New).
-
Korea National University of Arts
The Korea National University of Arts affiliated with the Ministry of Culture, Sports, and Tourism was established in 1993 to train professional artists with a focus on practical skills. In 1993, it opened the School of Music in Seocho-gu, Seoul, followed by the School of Drama in 1994 and the School of Film, TV & Multimedia in 1995. In 1996, the School of Dance was opened at the building in Seokgwan-dong, Seongbuk-gu, Seoul. The School of Visual Arts was installed at the Seokgwan-dong building in 1997. With the addition of the School of Korean Traditional Arts, Korea National University of Arts came to be equipped with six schools. With the goal of fostering professional artists in South Korea, it has adopted a unique entrance examination departing from the existing university entrance examinations in an effort to discover new talents. It has also focused on creating educational environment in which students can maximize their artistic potential. Although it retains a format of a school, it has been operated as an affiliate to the Ministry of Culture, Sports, and Tourism since 1998 instead of the Ministry of Education. The School of Visual Arts has Department of Visual Arts, Department of Design, Department of Architecture, and Department of Art Theory. Korea National University of Arts has actively provided education for fostering international artists by running various international exchange programs and inviting globally renowned artists to teach classes.