Image provided by SPACE 21
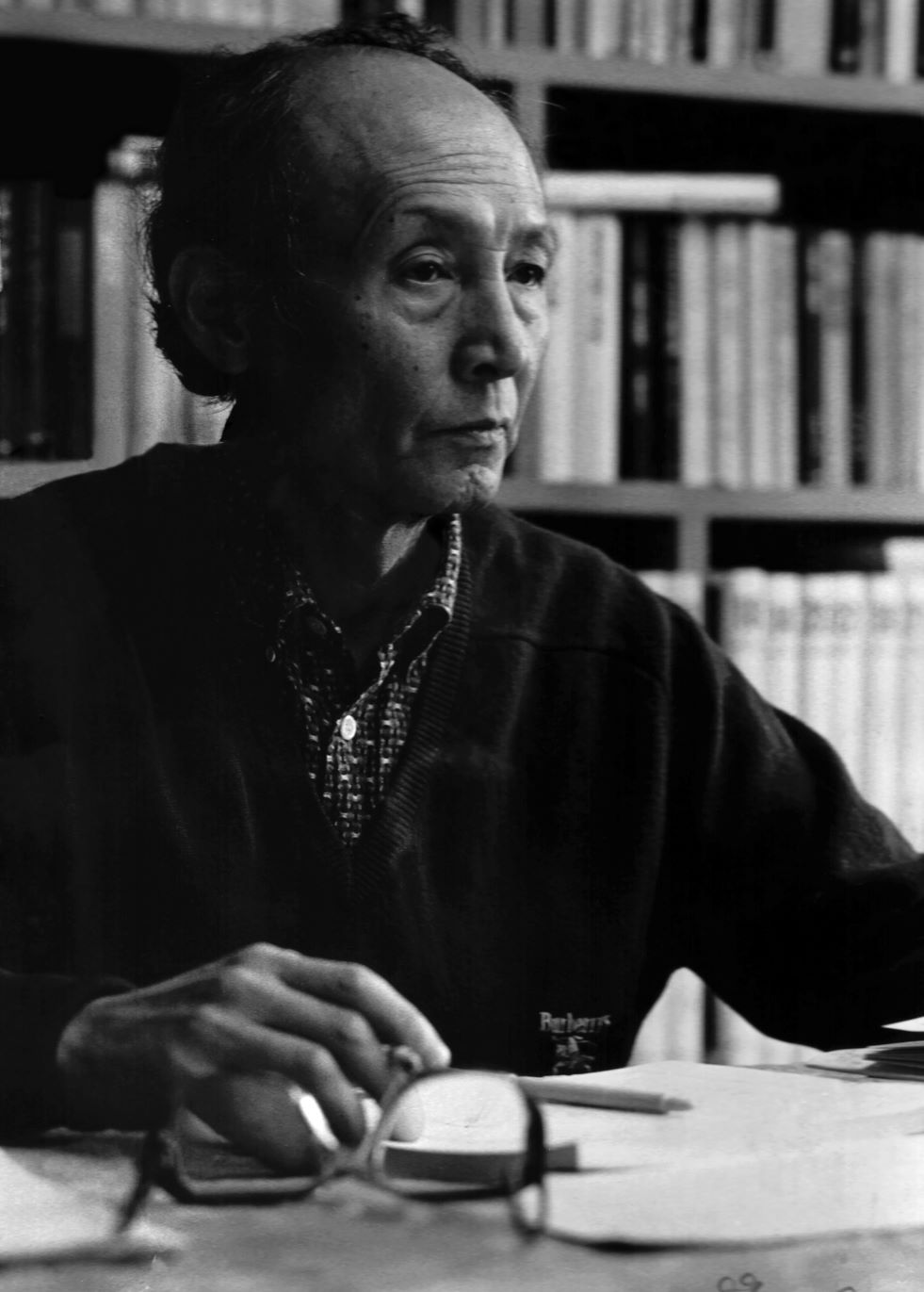
Lee Yil
* Source: MMCA
Related
-

Korean Avant Garde Association (AG)
An art group formed in 1969 and active until 1975 that promoted avant-garde art. The group elevated the concept of avant-garde to the forefront of Korean contemporary art. It’s members explored and developed new style of sculpture, and sought to contribute to the development of a new Korean art culture. The group published the periodical AG, which centered on artists, sculptors, and art critics in their thirties, and through the periodical, the group introduced new oversea trends to Korea and explored the theory and concepts behind avant-garde aesthetics. The group is regarded as responsible for introducing conceptual and formal diversity to Korean contemporary art, through a transition of artistic values, the active use of new materials, and helping to foment a wider public understanding of new trends within contemporary art.
-

International Biennial Exhibition of Prints in Tokyo
The International Biennial Exhibition of Prints in Tokyo was an international print exhibition held in Japan eleven times from 1957 through 1979. Initially, it was co-hosted by The National Museum of Modern Art, Tokyo and The Yomiuri Shimbun newspaper company. In the fifth edition, the International Cultural Promotion Association (Kokusai bunka shinkōkai) replaced The Yomiuri Shimbun, strengthening the nature of cultural exchange. Over twenty-two years, a total of 1,317 artists (1,098 foreign artists and 219 Japanese artists) participated in the International Biennial Exhibition of Prints in Tokyo, with approximately 3,000 works submitted. The International Biennial Exhibition of Prints in Tokyo is one of the international exhibitions in which a large number of Korean artists took part. This is partly owing to geographical proximity, but active exchanges with Japanese art circles in the 1970s also encouraged their participation. Korean artists consistently participated from the fifth edition to the eleventh. Yoo Kangyul, Kim Chonghak, and Youn Myeungro joined the fifth edition (1966); Bae Yoong, Suh Seungwon, and Ahn Dongguk, the sixth edition (1968); Kim Tchahsup, Ha Chonghyun, and Lee Ufan, the seventh edition (1970); Kim Sangyu, Kim Tschang-yeul, and Kwak Duckjun, the eighth edition (1972); Lee Ufan, Kim Kulim, and Chung Chanseung, the ninth edition (1974); Lee Kangso, the tenth edition (1976); and Suh Seungwon, Shim Moonseup, Kwak Duckjun, Chin Ohcsun, and Lee Ufan, the eleventh (1979). Among these participating artists, Kim Chonghak received an honorable mention in the fifth, and Kwak Duckjun won the Minister of Education Award in the eighth. In the eleventh, Chin Ohcsun won the Minister of Foreign Affairs Award and Lee Ufan won the Kyoto National Modern Art Award. In the eighth, the art critic Lee Il participated as an international judge. The International Biennial Exhibition of Prints in Tokyo exerted a considerable influence upon the development of Japanese contemporary prints and played a role in anchoring prints in the postmodern discourse of “de-genre” and “de-media” in conjunction with contemporary art. Witnessing the interest in prints not just from Japanese art circles but also from the international art community through the exhibitions, Korean artists became more interested than ever in prints, which emerged as a major medium of expression in contemporary art. Since the 1970s, there has been a significant increase in the number of artists working in printmaking.
-

Department of Art at Hongik University
Established in 1949, the Department of Art at Hongik University consists of one art theory department and eleven practice-based departments, including painting, Oriental painting, printmaking, sculpture, woodworking and furniture design, metal art and design, ceramics and glass, textile art and fashion design, visual communication design, and industrial design. In 1955, it moved from Jongro-gu, Seoul to the current location in Sangsu-dong, Mapo-gu, Seoul. The history of the College of Fine Arts can be largely divided into the period of the Department of Fine Arts from 1949 through 1953, the period of the School of Fine Arts from 1954 through 1971, and the period of the College of Fine Arts from 1972 until now. In March 1953, the Department of Fine Arts produced the first six graduates, and in the following year the School of Fine Arts with three departments was established. In December 1971, it was upgraded to a college, which exists up to the present. Several exhibitions organized by its graduates are notable, including the Four Artists Exhibition held in 1956 as the first anti-National Art Exhibition (Daehanminguk misul jeollamhoe or Gukjeon) by the third and fourth classes of graduates and the Union Exhibition of Korean Young Artists held in 1967 by graduates from the 1960s as an effort to realize experimental art.
Find More
-

Lee Kyungsung
Lee Kyungsung (1919-2009, pen name Seoknam) was born in Incheon as the first son of Lee Hak-soon and Jin Bo-bae. He graduated from Changyeong Elementary School (1926-31) and Gyeongseong Commercial School (1934-36). In 1937, he moved to Japan and graduated from the Department of Law at Waseda University in 1941. After his return to Korea, he worked as a clerk at the Gyeongseong Court. Later, he returned to Japan to study art history at Weseda University. After independence, he was appointed as the first director of the Incheon City Museum, a director of Hongik University Museum, Walker Hill Art Center (1981-83), and the MMCA (1981-83, 1986-92). He strived to improve the structure of Korean art museums and also trained professional curators. During his appointment as a professor at Ewha Womans University (1957-60) and Hongik University (1961-81), he also served as a chair of the Korean Art Critics Association and published several important books that contributed to the foundation of a modern Korean art history. He established the Seoknam Art Culture Foundation in 1989 and the Seoknam awards for art and art theory. After his retirement, he focused on his art and held numerous solo exhibitions.
-

Lee Gu-yeol
Lee Gu-yeol(1932-2020) was the first art journalist, an art critic, and a researcher of modern art in Korea. Born in Yeonbaek, Hwanghae-do Province, Lee went to South Korea during the Korean War. He enlisted in the army as a cadet, completed infantry and artillery schools, and served as an officer during the war. After being discharged as a captain in 1958, he joined World Telecommunications and worked in the publications department. In 1959, he enrolled as a junior in the College of Fine Arts at Hongik University, but he could not finish his studies. He worked as an art reporter in the culture desk of Segye Ilbo newspaper (renamed the Minguk Ilbo in 1960) and then as a reporter and deputy head of the culture desk of Kyunghyang Shinmun newspaper in and after 1962. In 1970, he transferred to Seoul Sinmun newspaper and served as the head of its culture desk. He became the head of the culture desk of Daehan Ilbo newspaper in 1972 but ended his journalistic career when the company ceased to publish in 1975. In 1964, Lee was in charge of editing the quarterly magazine Misul (Art) (published by Munhwa Gyoyuk Chulpansa). He also organized the publication of fifteen volumes of the Complete Collection of Korean Art (sponsored by Donghwa Chulpan Gongsa) and worked as chief editor from 1973 through 1975. He served as president of the Korean Art Critics Association (1984–1985), a member of the Cultural Heritage Committee of the Ministry of Culture and Tourism (1992–1999), and as director of exhibition projects at the Seoul Arts Center (1993–1996). He also opened the Korean Modern Art Research Institute and published its irregular periodical Modern Art of Korea from the first to fifth issues (1975–1977). His books include The Realm of Painting: The Life and Art of Idang (1968), A Study on Modern Korean Art (1972), The Development of Modern Korean Art (1982), Research on Modern Korean Art History (1992), History of Modern Korean Painting (1993), 50 Years of North Korean Art (2001), The Story behind Modern Korean Art (2005), Rha Hyeseok: The Woman Who Drew Her Fiery Life (2011), Korean Cultural Heritage: A History of Suffering (2013), and My Days as an Art Reporter (2014). In 2018, he published two volumes of his self-edited literary collection Miscellany by Cheongyeo to celebrate his turning eighty-eight. Lee Gyu-yeol played a crucial role in the establishment of the Archives of Korean Art Journal, the first art archives in Korea, in December 1998 by donating his materials related to modern and contemporary art to the Samsung Museum of Art. In 2015, he donated more than 4,000 items to Gacheon Museum of the Gil Cultural Foundation. He passed away in 2020 at the age of eighty-nine.
-
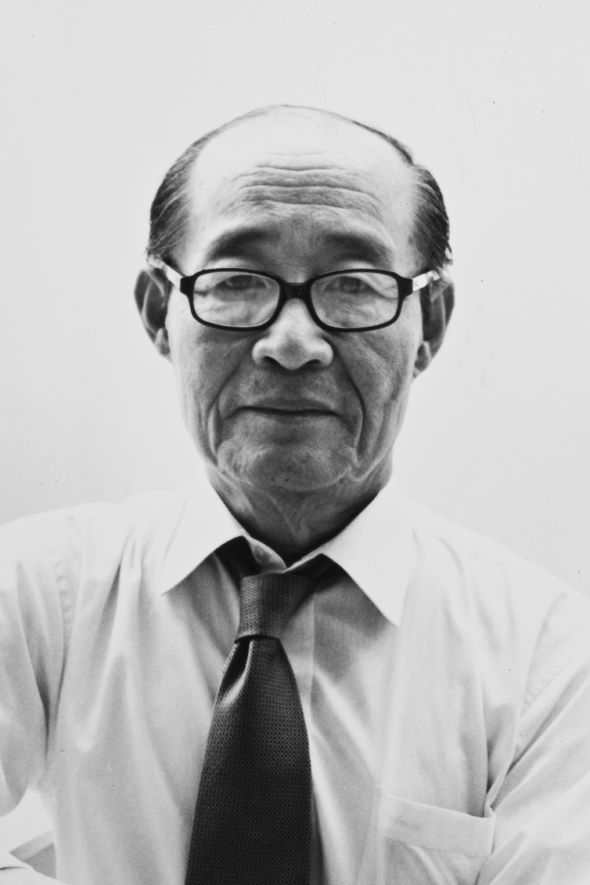

Yu Jun-sang
Yu Jun-sang (1932-2018) was a founding member of the Korean Art Critics Association [Hanguk misul pyeongnonga hyeophoe] along with Lee Yil and Oh Kwang-su. He has worked in various fields as a curator, educator, and art museum director. After graduating from the College of Commerce at Seoul National University in 1954, Yu moved to France in 1956 and pursued a Ph.D. in business administration at the University of Paris (Université de Paris) before dropping out. He studied painting at the Académie de la Grande Chaumière and audited the history of Western modern and contemporary art at the Liberal Arts Department of the University of Paris. After returning to Korea, he taught art theory courses at Hongik University, Seorabeol University of Arts, and Ewha Womans University. As an art critic, he served as president of the Korean Art Critics Association from 1972 to 1982. Yu participated in the selection of artists representing Korea for the exhibition of Contemporary Korean Painting held at The National Museum of Modern Art, Tokyo in 1968, and Korean Contemporary Art: 1957–1972 held at the Myeong-dong Gallery in 1973. He was head of the curatorial department at the National Museum of Contemporary Art, Korea (now MMCA) from 1986 to 1992 and as director of the Seoul Museum of Art from 1999 to 2002. He also laid the foundation for Korean art criticism by assuming charge of editing the magazines Hyeondae Misul of Myeong-dong Gallery in 1974 and Sun misul of Sun Gallery from 1979 through 1983. His publications can be divided into those that attempt a conceptual or aesthetic approach and those that discuss the works of other artists. The former include Korean Contemporary Art 12: Stylization of Korean Sentiments (Hanguk Ilbo newspaper company, 1977, 82–108) and “Prospects and Possibilities for Computer Art: A Focus on Patterns of Perception and Artistry” in Beyond Modernism (Yesul jisik, 1989, 298–315). Among the artists that Yu addressed with interest were Rhee Seundja, Kwon Jinkyu, Quac Insik, Moon Shin, Nam Kwan, Kwon Okyon, Kim Whanki, Chang Dookun, Lee Seduk, Han Mook, Moon Hakjin, Park Hangsup, Choi Youngrim, and Kim Sechoong. Yu was particularly interested in the generation of artists who had received art training before Korea’s liberation from Japan as well as those who had lived in France.