Image provided by National Museum of Korea
National Museum of Korea
* Source: Multilingual Glossary of Korean Art. Korea Arts Management Service
Related
-
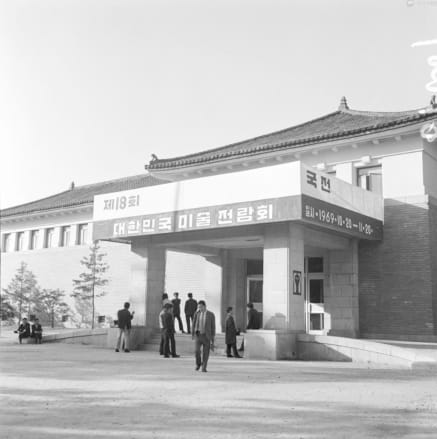

Gyeongbokgung Palace Museum
Gyeongbokgung Palace Museum was a national museum located in Gyeongbokgung Palace from 1949 to 1973. It was used as an exhibition hall for the National Art Exhibition (Gukjeon) of Korea. It became the Museum of the Japanese Government-General of Korea in 1939, then was used as a venue of the Joseon Art Exhibition until 1944 and became the Gyeongbokgung Palace Museum after Independence. In 1949, it was used for the first National Art Exhibition of Korea. It also hosted large scale exhibitions, such as the Science Exhibition, the National Middle and High School Student Art Exhibition, the International Children’s Art Exhibition, and the National Commercial and Industry Art Exhibition from the 1950s to the 1960s, especially when there were few public museums. In 1957, it hosted The Family of Man, a photographic exhibition which travelled around the world starting at the Museum of Modern Art in New York City. The Gyeongbokgung Palace Museum was also the base of the National Museum of Contemporary Art from 1969 until its relocation to Deoksugung Palace in 1973. It was used as the National Folk Museum of Korea from 1975 to 1993 and was demolished during the restoration project of Gyeongbokgung Palace in 1998.
-
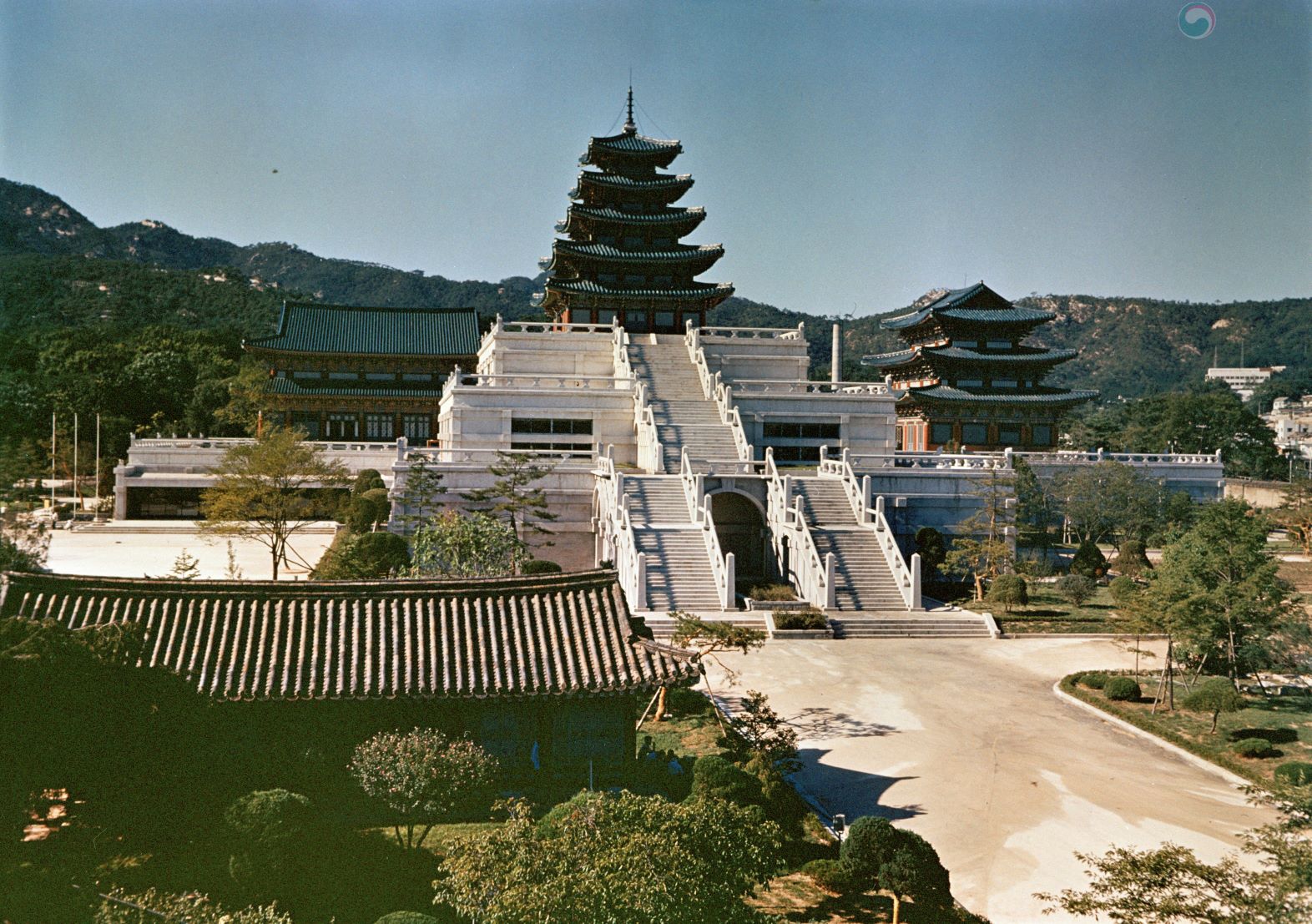

National Museum
The National Museum was established by the Korean government in 1945 after Independence. It consists of a general museum and a special museum. The National Museum of Korea as a general museum took over the Museum of the Japanese Government-General of Korea and opened at Gyeongbokgung Palace in 1945. It annexed the Gyeongju, Buyeo, Gongju, and Kaesong museums. It also annexed Song Seokha’s National Museum of Anthropology and accepted the collection of Deoksugung Museum of Art (former Yi Royal Family Museum) in 1969. The museum was called “National Museum” from 1945 to 1972, and the “National Museum, of Korea” after the reorganization in 1972. Meanwhile, local annex museums were upgraded to local national museums, such as Gyeongju National Museum and Buyeo National Museum. Since Independence, national museums have been constructed in many local cities, including Gyeongju, Buyeo, Gongju, Gwangju, Jinju, Cheongju, Jeonju, Daegu, Gimhae, Jeju, Chuncheon, Naju, and Iksan. These museums play pivotal roles in maintaining local histories and cultures. Special museums within the National Museum of Korea include the National Palace Museum (the history and culture of the Joseon Dynasty), the Maritime Museum (maritime culture), the Forest Museum, the Diplomatic Museum, the Police Museum, the Custom Museum, the Lighthouse Museum, the Postal Museum, and the Museum of Korean Traditional Music.
Find More
-
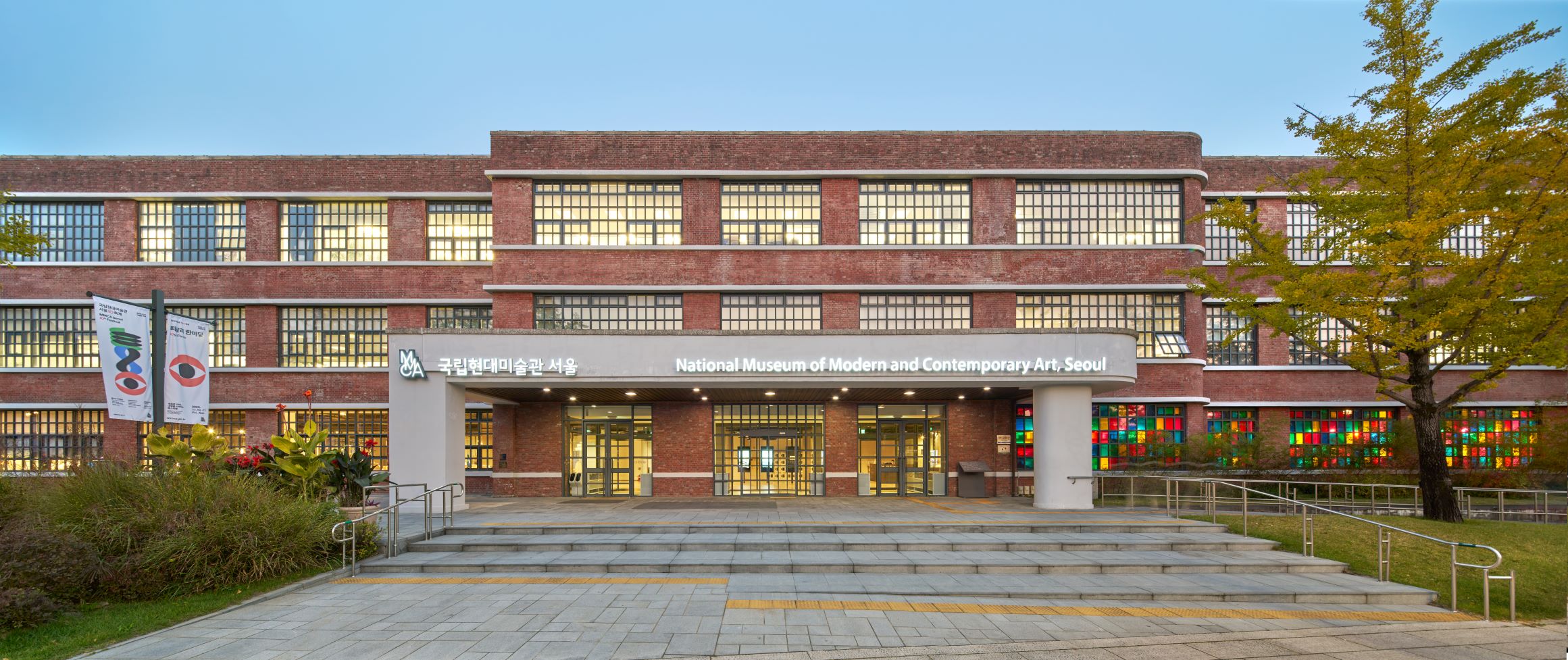

National Museum of Modern and Contemporary Art, Korea (MMCA)
A national museum established in 1969 that researches, collects, and exhibits modern and contemporary art. As of 2018, there are branches in Gwacheon, Deoksugung, Seoul, and Cheongju. When first established, the National Museum of Modern Art (now MMCA) was located within Gyeongbokgung palace. In 1973, the museum moved to the East Wing of the Deoksugung Seokjojeon building. Then, in 1986, the museum moved to its current location in Gwacheon, to occupy a new building equipped with an outdoor sculpture exhibition space, and has since opened a new chapter in Korean art. The perceived need for a space to focus specifically on Korean contemporary art led to the establishment of further site, the National Museum of Contemporary Art, Deoksugung in 1998. In November 2013, a further demand for contemporary art exhibitions led to the establishment of another Seoul branch being created in the Defense Security Command building in Sogyeok-dong, Jongno-gu, which has since its inception engaged in multifaceted exhibitions of both domestic and overseas contemporary art. Also, as a further component of the MMCA complex, a disused tobacco factory in Cheongju was remodeled to provide a home to the National Art Storage Center.
-
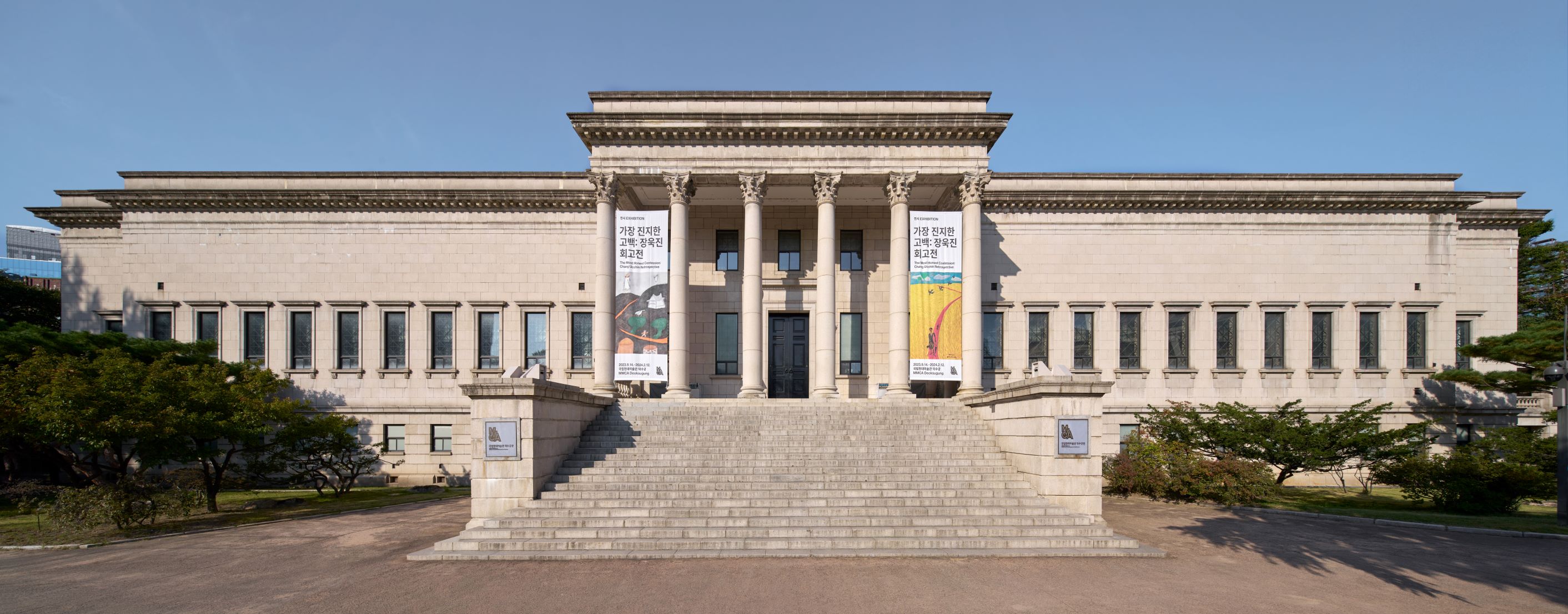

Deoksugung Museum of Art
A term that refers to two separate art museums that have existed in the grounds of Deoksugung palace at different times. First, the Yi Royal Family Museum, which was built in 1938 and renamed the Deoksugung Museum of Art after independence in 1948. This iteration of the Museum was merged with the National Museum of Korea in 1969. Separately, in 1998 a branch of the National Museum of Contemporary Art, Korea (now MMCA) was established at this location, and also named the Deoksugung Museum of Art. In 2013, the official name of the branch was changed to the National Museum of Modern and Contemporary Art, Deoksugung but some people still use the previous name, Deoksugung Museum of Art.