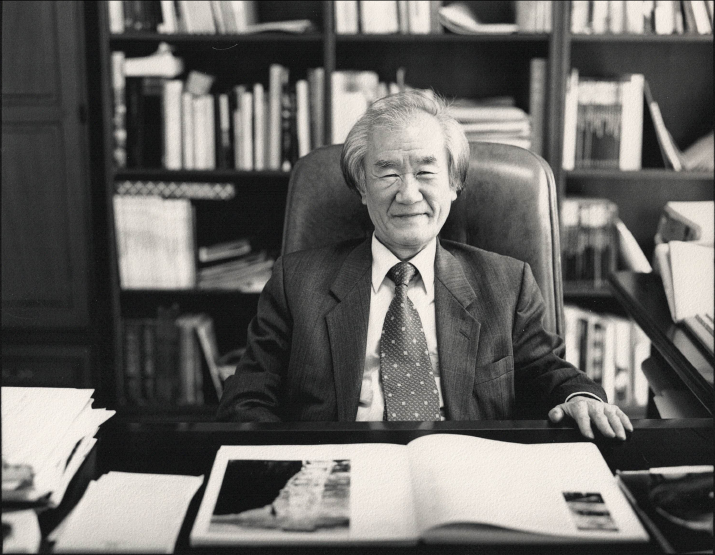
Image provided by Kim Yoon-Soo Archive
Kim Yoon-Soo
* Source: MMCA
Related
-

Minjung Art
An artistic movement that came to prominence alongside Korea’s democratization movement in the 1980s. Minjung artists often sought to critically portray the violent repression and corruption of the military dictatorship, to represent the experiences of laborers and farmers, and to achieve social change through art. In contrast to abstraction, which constituted the mainstream of 1970s art in Korea, Minjung Art is notable for the use of representational and figurative forms. One possible point of origin for Minjung Art is Oh Yoon’s work in the Reality Group (Hyeonsil dongin). The group was formed in 1969 by Kim Ji-ha, Oh Yoon, and Lim Se-taek. A variety of Minjung art groups were established, including the Reality and Utterance (Hyunsilgwa bareon) in 1979 by Kim Jungheun, Oh Yoon, Joo Jae-hwan, art critic Sung Wan-kyung, and Choi Min, the Gwangju Freedom Artist Association (Gwangju jayu misulin hyeopuihoe) in 1979 by Hong Sungdam and Choi Youl, the Imsulnyeon (The Year Imsul) in 1982, and the Dureong in 1983. These groups all commonly critiqued Western capitalism. In terms of form, Minjung artists adopted traditional and ethnic folk modes of expression using diverse media such as collage, printmaking, oil painting, and photography. Following the 15 Years of Korean Minjoong Arts: 1980-1994 Exhibition at the National Museum of Modern and Contemporary Art, Minjung Art became an accepted part of Korean art history. Overseas, Minjung Art has also become a recognized term that describes this genre and its unique focus on the political and social history of Korea.
-
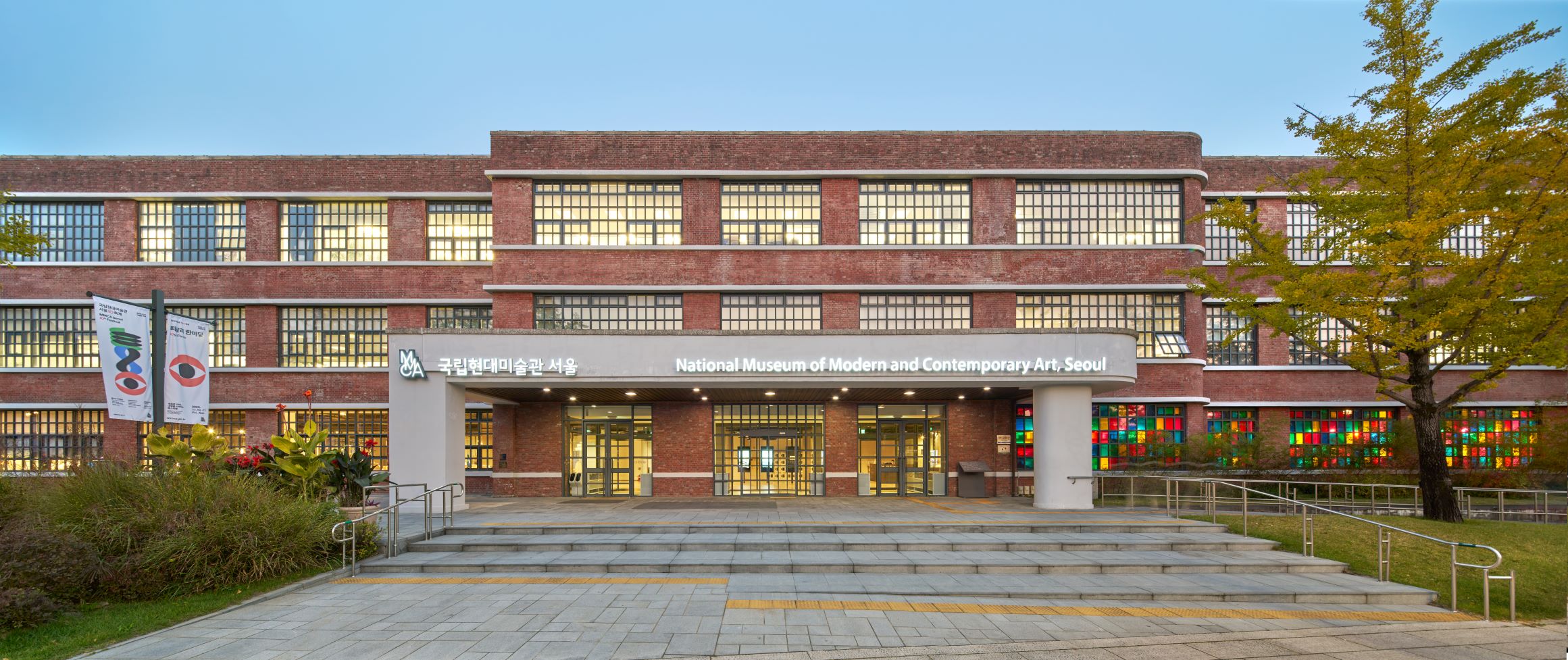

National Museum of Modern and Contemporary Art, Korea (MMCA)
A national museum established in 1969 that researches, collects, and exhibits modern and contemporary art. As of 2018, there are branches in Gwacheon, Deoksugung, Seoul, and Cheongju. When first established, the National Museum of Modern Art (now MMCA) was located within Gyeongbokgung palace. In 1973, the museum moved to the East Wing of the Deoksugung Seokjojeon building. Then, in 1986, the museum moved to its current location in Gwacheon, to occupy a new building equipped with an outdoor sculpture exhibition space, and has since opened a new chapter in Korean art. The perceived need for a space to focus specifically on Korean contemporary art led to the establishment of further site, the National Museum of Contemporary Art, Deoksugung in 1998. In November 2013, a further demand for contemporary art exhibitions led to the establishment of another Seoul branch being created in the Defense Security Command building in Sogyeok-dong, Jongno-gu, which has since its inception engaged in multifaceted exhibitions of both domestic and overseas contemporary art. Also, as a further component of the MMCA complex, a disused tobacco factory in Cheongju was remodeled to provide a home to the National Art Storage Center.
-

Reality Group
An artists’ group concerned with the creation of a national aesthetic and realism. The group was formed by Oh Yoon, Lim Setaek, and Oh Kyunghwan, who were students at the Seoul National University College of Fine Arts in 1969. The inaugural exhibition of Reality Group was originally planned to be held at the Sinmunhoegwan Gallery from October 25 to 31, 1969, but the exhibition was canceled due to pressure from local authorities, after it was reported to the government by the university. However, knowledge about the existence of the group and its aims resulted from the inclusion of the 1st Declaration of the Reality Group (written by aesthetics major Kim Jiha and edited by Kim Yoon-Soo) in the catalogue for the inaugural exhibition. The stated goal of the Reality Group was to establish a new national art theory based on realist art that could usefully account for Korean tradition of visual culture. This influence of this approach was kept alive through Oh Yoon’s participation in the Reality and Utterance (Hyunsilgwa bareon) of the 1980s.
Find More
-

Lee Gu-yeol
Lee Gu-yeol(1932-2020) was the first art journalist, an art critic, and a researcher of modern art in Korea. Born in Yeonbaek, Hwanghae-do Province, Lee went to South Korea during the Korean War. He enlisted in the army as a cadet, completed infantry and artillery schools, and served as an officer during the war. After being discharged as a captain in 1958, he joined World Telecommunications and worked in the publications department. In 1959, he enrolled as a junior in the College of Fine Arts at Hongik University, but he could not finish his studies. He worked as an art reporter in the culture desk of Segye Ilbo newspaper (renamed the Minguk Ilbo in 1960) and then as a reporter and deputy head of the culture desk of Kyunghyang Shinmun newspaper in and after 1962. In 1970, he transferred to Seoul Sinmun newspaper and served as the head of its culture desk. He became the head of the culture desk of Daehan Ilbo newspaper in 1972 but ended his journalistic career when the company ceased to publish in 1975. In 1964, Lee was in charge of editing the quarterly magazine Misul (Art) (published by Munhwa Gyoyuk Chulpansa). He also organized the publication of fifteen volumes of the Complete Collection of Korean Art (sponsored by Donghwa Chulpan Gongsa) and worked as chief editor from 1973 through 1975. He served as president of the Korean Art Critics Association (1984–1985), a member of the Cultural Heritage Committee of the Ministry of Culture and Tourism (1992–1999), and as director of exhibition projects at the Seoul Arts Center (1993–1996). He also opened the Korean Modern Art Research Institute and published its irregular periodical Modern Art of Korea from the first to fifth issues (1975–1977). His books include The Realm of Painting: The Life and Art of Idang (1968), A Study on Modern Korean Art (1972), The Development of Modern Korean Art (1982), Research on Modern Korean Art History (1992), History of Modern Korean Painting (1993), 50 Years of North Korean Art (2001), The Story behind Modern Korean Art (2005), Rha Hyeseok: The Woman Who Drew Her Fiery Life (2011), Korean Cultural Heritage: A History of Suffering (2013), and My Days as an Art Reporter (2014). In 2018, he published two volumes of his self-edited literary collection Miscellany by Cheongyeo to celebrate his turning eighty-eight. Lee Gyu-yeol played a crucial role in the establishment of the Archives of Korean Art Journal, the first art archives in Korea, in December 1998 by donating his materials related to modern and contemporary art to the Samsung Museum of Art. In 2015, he donated more than 4,000 items to Gacheon Museum of the Gil Cultural Foundation. He passed away in 2020 at the age of eighty-nine.
-

Lee Kyungsung
Lee Kyungsung (1919-2009, pen name Seoknam) was born in Incheon as the first son of Lee Hak-soon and Jin Bo-bae. He graduated from Changyeong Elementary School (1926-31) and Gyeongseong Commercial School (1934-36). In 1937, he moved to Japan and graduated from the Department of Law at Waseda University in 1941. After his return to Korea, he worked as a clerk at the Gyeongseong Court. Later, he returned to Japan to study art history at Weseda University. After independence, he was appointed as the first director of the Incheon City Museum, a director of Hongik University Museum, Walker Hill Art Center (1981-83), and the MMCA (1981-83, 1986-92). He strived to improve the structure of Korean art museums and also trained professional curators. During his appointment as a professor at Ewha Womans University (1957-60) and Hongik University (1961-81), he also served as a chair of the Korean Art Critics Association and published several important books that contributed to the foundation of a modern Korean art history. He established the Seoknam Art Culture Foundation in 1989 and the Seoknam awards for art and art theory. After his retirement, he focused on his art and held numerous solo exhibitions.
-
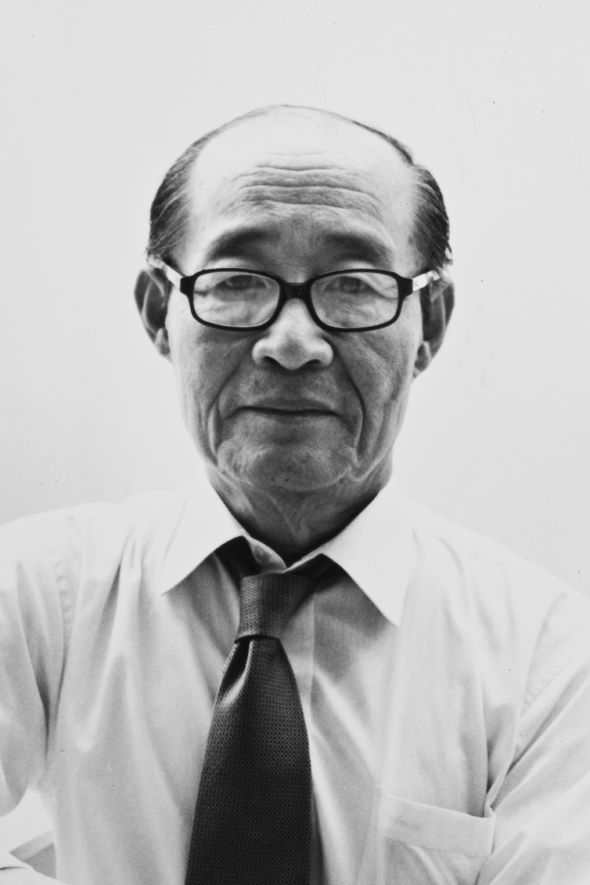

Yu Jun-sang
Yu Jun-sang (1932-2018) was a founding member of the Korean Art Critics Association [Hanguk misul pyeongnonga hyeophoe] along with Lee Yil and Oh Kwang-su. He has worked in various fields as a curator, educator, and art museum director. After graduating from the College of Commerce at Seoul National University in 1954, Yu moved to France in 1956 and pursued a Ph.D. in business administration at the University of Paris (Université de Paris) before dropping out. He studied painting at the Académie de la Grande Chaumière and audited the history of Western modern and contemporary art at the Liberal Arts Department of the University of Paris. After returning to Korea, he taught art theory courses at Hongik University, Seorabeol University of Arts, and Ewha Womans University. As an art critic, he served as president of the Korean Art Critics Association from 1972 to 1982. Yu participated in the selection of artists representing Korea for the exhibition of Contemporary Korean Painting held at The National Museum of Modern Art, Tokyo in 1968, and Korean Contemporary Art: 1957–1972 held at the Myeong-dong Gallery in 1973. He was head of the curatorial department at the National Museum of Contemporary Art, Korea (now MMCA) from 1986 to 1992 and as director of the Seoul Museum of Art from 1999 to 2002. He also laid the foundation for Korean art criticism by assuming charge of editing the magazines Hyeondae Misul of Myeong-dong Gallery in 1974 and Sun misul of Sun Gallery from 1979 through 1983. His publications can be divided into those that attempt a conceptual or aesthetic approach and those that discuss the works of other artists. The former include Korean Contemporary Art 12: Stylization of Korean Sentiments (Hanguk Ilbo newspaper company, 1977, 82–108) and “Prospects and Possibilities for Computer Art: A Focus on Patterns of Perception and Artistry” in Beyond Modernism (Yesul jisik, 1989, 298–315). Among the artists that Yu addressed with interest were Rhee Seundja, Kwon Jinkyu, Quac Insik, Moon Shin, Nam Kwan, Kwon Okyon, Kim Whanki, Chang Dookun, Lee Seduk, Han Mook, Moon Hakjin, Park Hangsup, Choi Youngrim, and Kim Sechoong. Yu was particularly interested in the generation of artists who had received art training before Korea’s liberation from Japan as well as those who had lived in France.