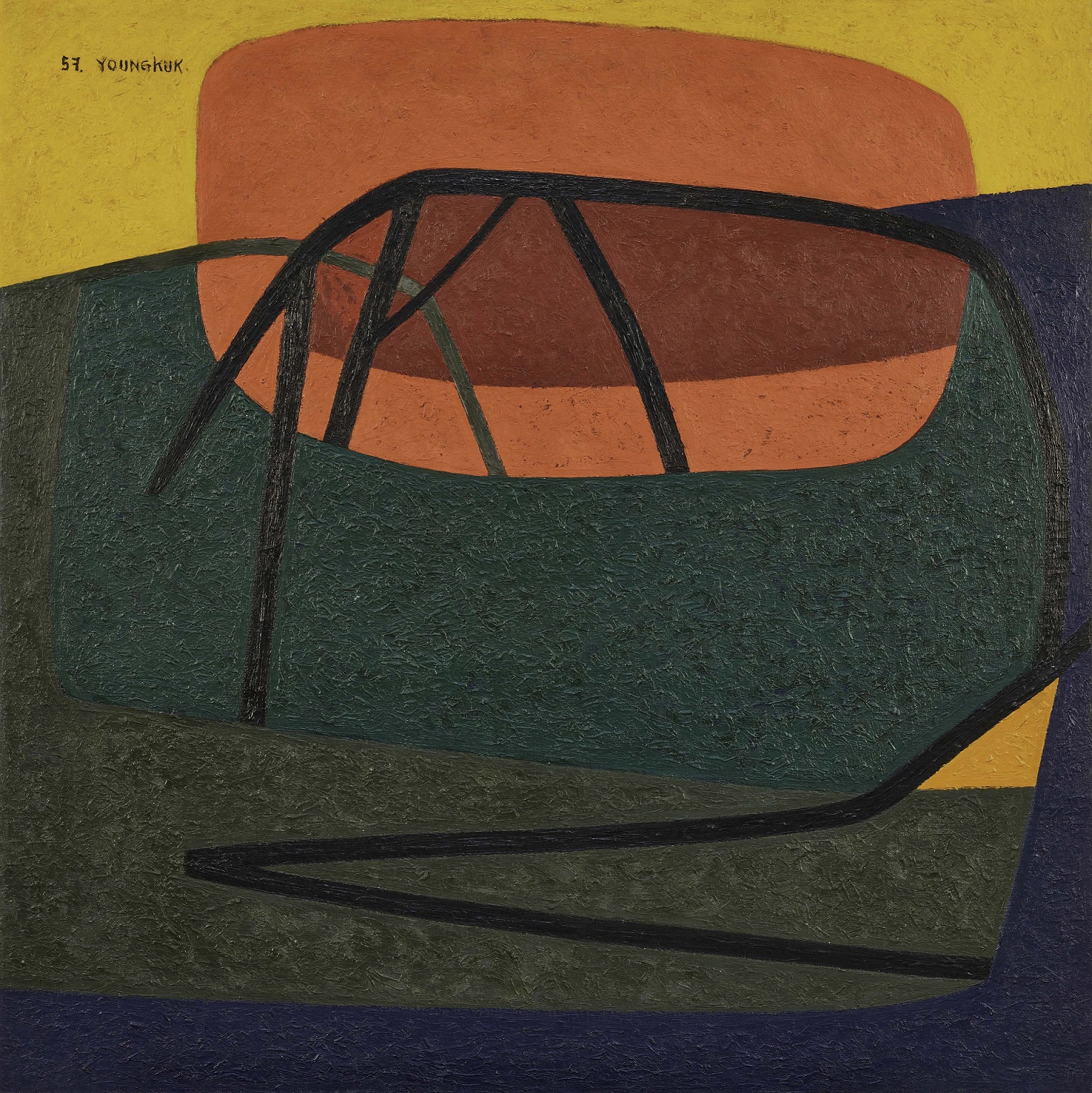
Yoo Youngkuk, Work, 1957, Oil on canvas, 101×101cm. MMCA collection
Yoo Youngkuk
* Source: Multilingual Glossary of Korean Art. Korea Arts Management Service
Related
-

Abstract art
A term which can be used to describe any non-figurative painting or sculpture. Abstract art is also called non-representational art or non-objective art, and throughout the 20th century has constituted an important current in the development of Modernist art. In Korea, Abstract art was first introduced by Kim Whanki and Yoo Youngkuk, students in Japan who had participated in the Free Artists Association and the Avant-Garde Group Exhibition during the late 1930s. These artists, however, had little influence in Korea, and abstract art flourished only after the Korean War. In the 1950s so called “Cubist images,” which separated the object into numerous overlapping shapes, were often described as Abstractionist, but only with the emergence of Informel painting in the late 1950s could the term “abstract” be strictly used to describe the creation of works that did not reference any exterior subject matter. The abstract movements of geometric abstractionism and dansaekhwa dominated the art establishment in Korea in the late-1970s. By the 1980s, however, with the rising interest in the politically focused figurative art of Minjung, abstraction was often criticized as aestheticist, elitist, and Western-centric.
-

Sinsanghoe
A group established through an alliance of a total of 23 artists and sculptors. Some were members of the Modern Art Association and Creative Art Association, some belonged to Sinjohyeongpa, and the rest were otherwise unaffiliated. The first exhibition was organized into the painting and sculpture divisions, while the design division was established starting with the second exhibition. The group sought to discover upcoming artists by holding contests, but it eventually disbanded after its seventh exhibition in 1968. The leadership comprised Lee Daiwon, Yoo Youngkuk, and Lee Bongsang. The painters included Kim Changeuk, Moon Woosik, Park Soukho, Park Changdorn, Park Hangsup, Son Dongchin, Lee Daljoo, Lee Joon, Lim Wangyu, Chung Keonmo, Choi Dukhyu, Han Bongduk, and Hwang Yooyup; the sculptors included Min Bokjin, Jeun Loijin, Kim Youngjung, and Kim Younghak; and Han Hongtaik was the craftsman and designer.
-

1950 Art Association
An alliance of artist associations established in 1950 by representatives Kim Whanki, Nam Kwan, and Lee Qoede and secretary general Kim Byungki. Groups excluding the Great Korean Art Association [Daehan misul hyeophoe] formed the 1950s Art Association for deconstruction for the purpose of the development and promotion of national art. While differing perspectives exist on the exact mission of the association, it is often considered to have embodied the desire of these established artists to progressively develop national art, regardless of their ideological differences. The association planned an exhibition for July 1, 1950, but it failed to come to fruition because of the outbreak of the Korean War. While the association was active for a short period of time, it left behind a legacy of public education programs on art theory, through endeavors such as initiating a series of lectures on contemporary painting. The solidification of the anti-communist agenda during the war caused the majority of the members of the Korea Art Alliance to depart for North Korea, and others, with the exception of Kim Whanki and Nam Kwan, joined the Great Korean Art Association. The association is therefore seen as an independent organization that opposed the establishment authority centered on the National Art Exhibition (Gukjeon).
Find More
-

International Biennial Exhibition of Prints in Tokyo
The International Biennial Exhibition of Prints in Tokyo was an international print exhibition held in Japan eleven times from 1957 through 1979. Initially, it was co-hosted by The National Museum of Modern Art, Tokyo and The Yomiuri Shimbun newspaper company. In the fifth edition, the International Cultural Promotion Association (Kokusai bunka shinkōkai) replaced The Yomiuri Shimbun, strengthening the nature of cultural exchange. Over twenty-two years, a total of 1,317 artists (1,098 foreign artists and 219 Japanese artists) participated in the International Biennial Exhibition of Prints in Tokyo, with approximately 3,000 works submitted. The International Biennial Exhibition of Prints in Tokyo is one of the international exhibitions in which a large number of Korean artists took part. This is partly owing to geographical proximity, but active exchanges with Japanese art circles in the 1970s also encouraged their participation. Korean artists consistently participated from the fifth edition to the eleventh. Yoo Kangyul, Kim Chonghak, and Youn Myeungro joined the fifth edition (1966); Bae Yoong, Suh Seungwon, and Ahn Dongguk, the sixth edition (1968); Kim Tchahsup, Ha Chonghyun, and Lee Ufan, the seventh edition (1970); Kim Sangyu, Kim Tschang-yeul, and Kwak Duckjun, the eighth edition (1972); Lee Ufan, Kim Kulim, and Chung Chanseung, the ninth edition (1974); Lee Kangso, the tenth edition (1976); and Suh Seungwon, Shim Moonseup, Kwak Duckjun, Chin Ohcsun, and Lee Ufan, the eleventh (1979). Among these participating artists, Kim Chonghak received an honorable mention in the fifth, and Kwak Duckjun won the Minister of Education Award in the eighth. In the eleventh, Chin Ohcsun won the Minister of Foreign Affairs Award and Lee Ufan won the Kyoto National Modern Art Award. In the eighth, the art critic Lee Il participated as an international judge. The International Biennial Exhibition of Prints in Tokyo exerted a considerable influence upon the development of Japanese contemporary prints and played a role in anchoring prints in the postmodern discourse of “de-genre” and “de-media” in conjunction with contemporary art. Witnessing the interest in prints not just from Japanese art circles but also from the international art community through the exhibitions, Korean artists became more interested than ever in prints, which emerged as a major medium of expression in contemporary art. Since the 1970s, there has been a significant increase in the number of artists working in printmaking.
-
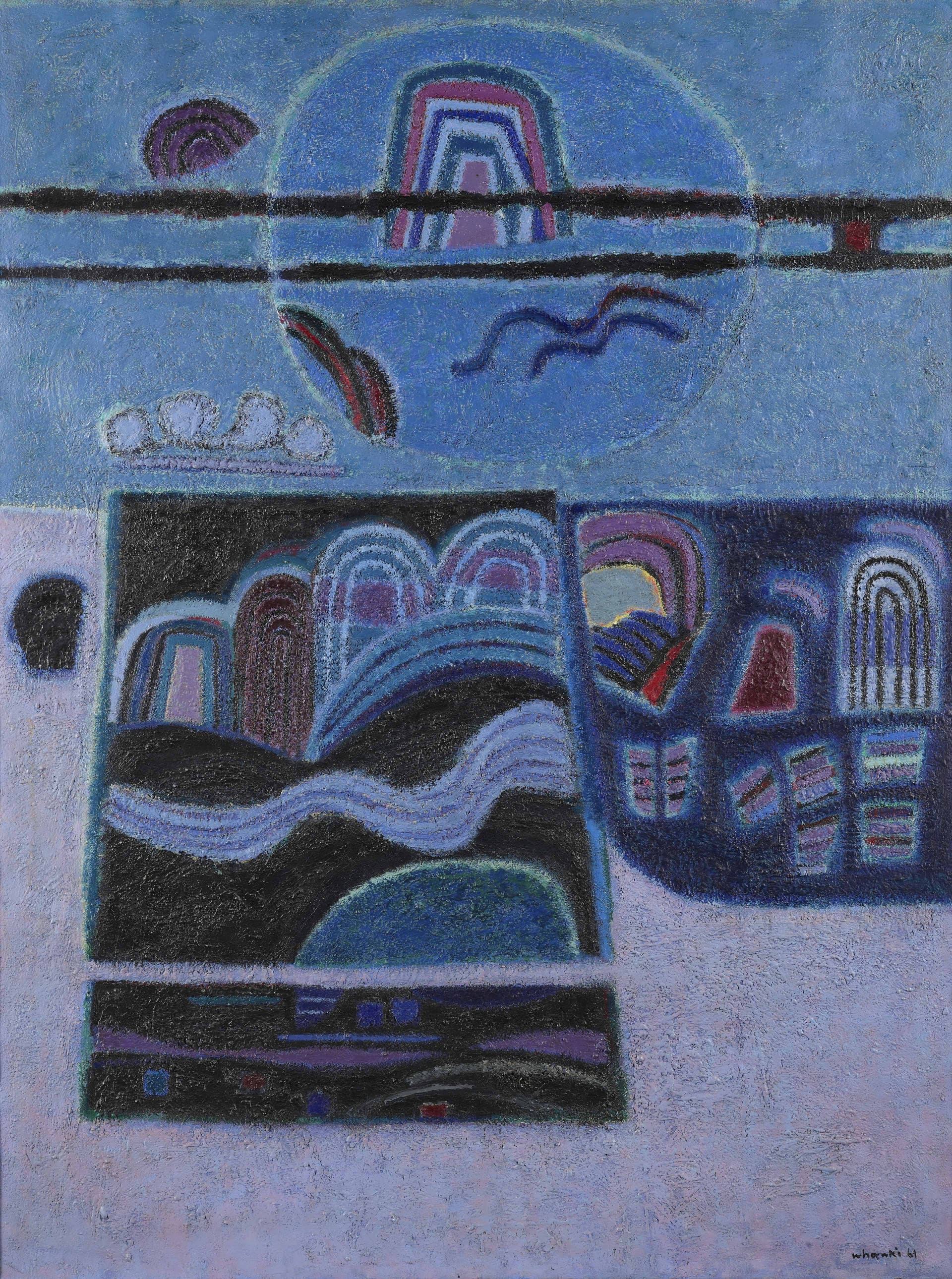

Kim Whanki
Kim Whanki (1913-1974, pen name Suhwa) was born in Sinan, Jeollanamdo, and his family origin was from Gimhae. He studied at the Department of Fine Arts at Nihon University, Tokyo, Japan from 1933 to 1936. He joined the Avant-Garde Western Art Institute in 1934 and submitted his work to Avant-Garde art associations, such as the Second Division Exhibition Nikaten (Nika Art Exhibition) and the Exhibition of the Free Artists Association (Jiyu Bijutsuka Kyokai). After independence, he organized the New Realism Group and worked as a professor in the Department of Fine Art at Seoul National University (1946-1950) and Hongik University (1952-55). He lived in Paris from 1956 to 1959, and after his return, he became a professor and later the Dean of the Fine Art College at Hongik University (1959-1963). He participated in the seventh Sao Paulo Biennale and won an honorary award, and then moved to New York. He abruptly passed away while having a solo exhibition at Poindexter Gallery, New York, ironically when his career in the US was at its peak. As a pioneer of Korean abstract art, he started by working in geometric abstraction and moved on to semi-abstract work that featured natural motifs such as the mountain, the moon, and the river. After moving to the U.S., he returned to abstraction with his so-called "dot paintings." His painting 16-Ⅳ-70 #166 Where, in What Form, Shall We Meet Again? (1970), was awarded a grand prize at the Korean Art Grand Award Exhibition and has inspired many contemporary Korean artists. His work Rondo (1938) was selected as No. 535 within the national Registered Cultural Properties.
-

International Biennial of Contemporary Color Lithography
The International Biennial of Contemporary Color Lithography was an international print exhibition held from 1950 through 1960 by the Cincinnati Art Museum in Ohio in the U.S. At the time, there was a printmaking boom in the U.S. sparked by the relocation of Atelier 17, a notable Parisian printmaking studio, to New York in 1940. In the 1950s and 1960s, the International Graphic Arts Society (IGAS) was founded, and several special exhibitions on prints were held, including New Expressions in Fine Printmaking: Ideas, Methods, and Materials (Brooklyn Museum, 1952). In addition, institutions for exploring printmaking, such as Pratt-Contemporaries Graphic Arts Center, Tamarind Lithography Workshop, and Universal Limited Art Edition (ULAE), were built. Under these circumstances, Gustave von Groschwitz, a curator of prints at the Cincinnati Art Museum from 1947 to 1963, organized the first biennial of color lithographs in the U.S. Only works created within two years could be submitted to the biennial, allowing two prints per artist. Korean artists had participated in the biennial since 1958. Yoo Kangyul, Kim Choungza, Choi Dukhyu, Kim Sou, Rhee Sangwooc, and Lee Hangsung took part in the fifth edition in 1958. Their participation in the biennial led to the acquisition of some works by the Cincinnati Art Museum. They were Face and Pagoda by Kim Sou, Winter by Rhee Sangwooc, and Silhouette and Buddha’s Spirit by Lee Hangsung. This marked the first overseas debut of contemporary Korean prints. In the sixth edition held in 1960, Mountain Sentiment and Revival by Lee Hangsung and Study by Bae Yoong won prizes. Starting in 1962, the International Biennial of Contemporary Color Lithography was held as a triennial and renamed International Prints.