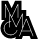Ryu Kyungchai, Neighborhood of a Bare Mountain, 1949, Oil on canvas, 94×129cm. MMCA collection
Ryu Kyungchai
* Source: Multilingual Glossary of Korean Art. Korea Arts Management Service
Related
-

Abstract art
A term which can be used to describe any non-figurative painting or sculpture. Abstract art is also called non-representational art or non-objective art, and throughout the 20th century has constituted an important current in the development of Modernist art. In Korea, Abstract art was first introduced by Kim Whanki and Yoo Youngkuk, students in Japan who had participated in the Free Artists Association and the Avant-Garde Group Exhibition during the late 1930s. These artists, however, had little influence in Korea, and abstract art flourished only after the Korean War. In the 1950s so called “Cubist images,” which separated the object into numerous overlapping shapes, were often described as Abstractionist, but only with the emergence of Informel painting in the late 1950s could the term “abstract” be strictly used to describe the creation of works that did not reference any exterior subject matter. The abstract movements of geometric abstractionism and dansaekhwa dominated the art establishment in Korea in the late-1970s. By the 1980s, however, with the rising interest in the politically focused figurative art of Minjung, abstraction was often criticized as aestheticist, elitist, and Western-centric.
-

College of Arts at Seoul National University
The College of Fine Arts of Seoul National University is located in Sillim-dong, Gwanak-gu, Seoul. According to the Decree on the Establishment of Seoul National University, the College of Art including the Department of Fine Arts and the Department of Music was founded in August 1946 at Seoul National University. The Department of Fine Arts consisted of sub-departments of Painting I, Painting II, Sculpture, and Design. It was organized by Chang Louis Pal and Lee Soonsuk. Chang Louis Pal had served as head of the Education and Management Bureau in the U.S. Army Military Government in Korea (USAMGIK) in Korea since December 1945. Lee Soonsuk assumed practical tasks as an advisor to the art section of the USAMGIK from 1946 when the Education and Management Bureau was changed to the Ministry of Culture and Education. In 1946, there were nine faculty members at the Department of Fine Arts in the College of Art: Chang Louis Pal, Kim Yongjun, Gil Jinseop, and Lee Jaehun as professors; Yun Seung-uk and Lee Soonsuk as associate professors; and Kim Whanki, Chang Woosoung, and Lee Byeonghyeon as assistant professors. However, after the incident of Korean students and professors’ protest against the U.S.’s attempt to merge several colleges and universities into a single university, Kim Yongjun, Gil Jinseop, and Kim Whanki resigned. In 1954, the College of Art was reorganized into the College of Fine Arts with three departments of painting, sculpture, and applied art. The Department of Aesthetics, which had temporarily belonged to the College of Fine Arts since 1948, was transferred to the College of Liberal Arts and Sciences in 1960. In 1963, according to the relocation plan of the Seoul National University main school building, the College of Fine Arts was moved to the former veterinary department building in Yeongeon-dong, Jongno-gu. In 1972, it was moved to the liberal arts department building in Hagye-dong, Seongbuk-gu, and then in 1976, to the current Gwanak campus. In 1981, the three departments of painting, sculpture, and applied art were reorganized into the five departments of Eastern painting, Western painting, sculpture, crafts, and industrial art. In 1989, the Department of Industrial Art was renamed the Department of Industrial Design, and in 1999, the Department of Crafts and the Department of Industrial Design were merged into the School of Design. Currently, the College of Fine Arts consists of the Department of Oriental Painting, Department of Painting, Department of Sculpture, Department of Craft, Department of Design, and Interdisciplinary Programs.
-

National Art Exhibition
A government-hosted exhibition held 30 times from 1949 to 1981, also known by the shorter name Gukjeon. Following national independence, the exhibition was the primary means for young and emergent Korean artists to achieve recognition. The influence of the exhibition declined as a result of the emergence of non-figurative art during the 1970s, the increased opportunities for artists to participate in overseas exhibitions, and the rise of private exhibitions and galleries.
Find More
-

Kim Kichang
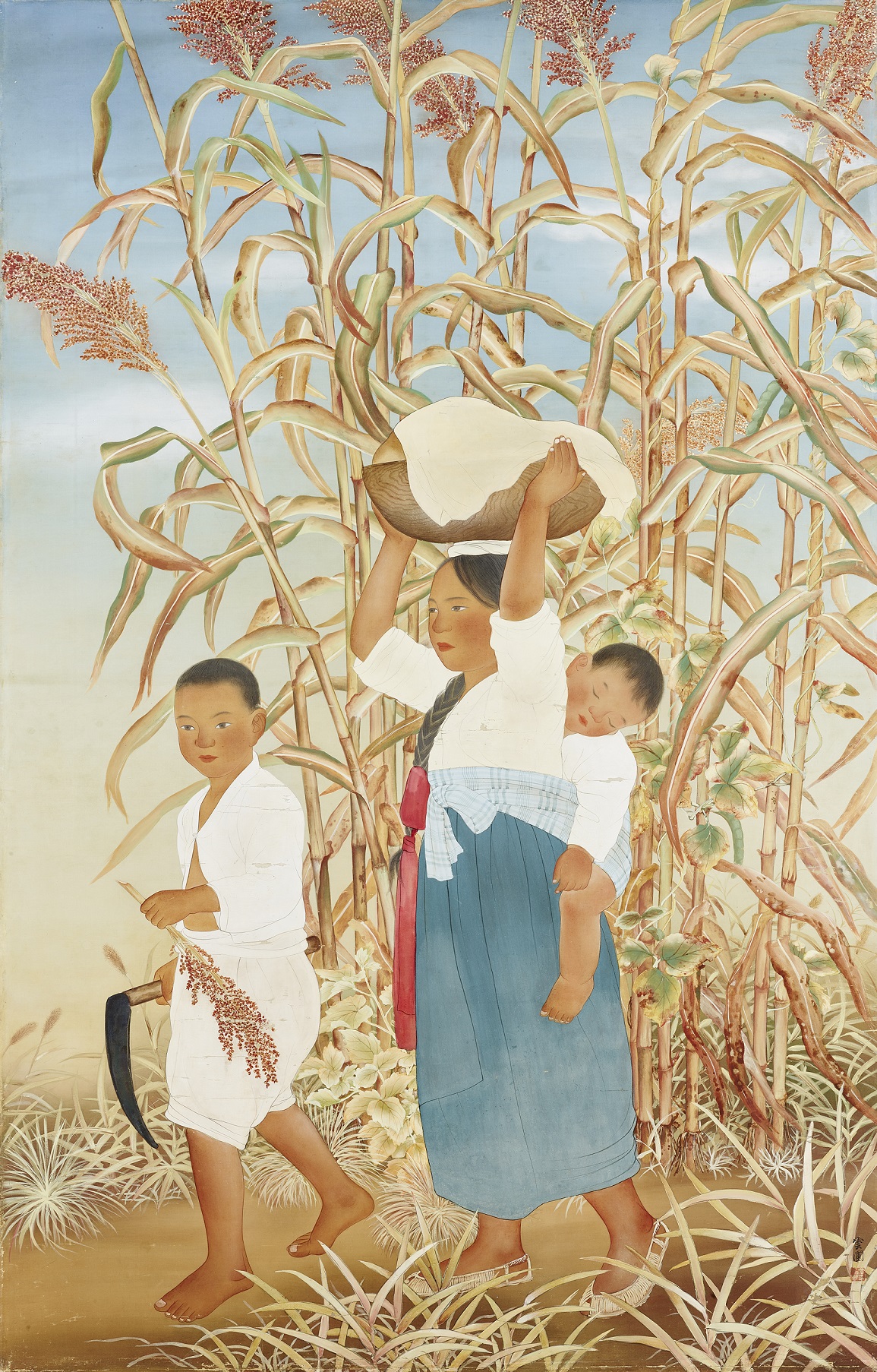
Kim Kichang (1913-2001, pen name Unpo or Unbo) studied Eastern painting at Kim Eunho’s art studio Nakcheongheon. After his debut in the tenth Joseon Art Exhibition [Joseon misul jeollamhoe] in 1931, he won special selections from 1937 to 1940, and became a renowned painter. He was appointed as the first president of Paek Yang Painting Association and became a professor at Hongik University and Soodo Women's Teachers College. He was awarded the Order of Civil Merit, Peony Medal in 1981 and the Korean Art Academy Award in 1983. After he passed away in 2001, he was awarded a posthumous Geumgwan Order of Culture Merit award. Although Kim initially focused on colorful figure paintings, following in the legacy of his mentor Kim Eunho, in his later career he collaborated with his wife Park Rehyun to modernize Korean painting by adopting cubism and abstraction. He reinterpreted traditional folk paintings in his representative works, such as Blue-green Landscape Painting series started in the 1970s and his Fool’s Landscape Painting in the 1980s and was inspired by portraits of historical figures. He contributed to the development of Korean modern art by working in an expanded formal territory from figuration to abstraction and addressing subject matter from folk painting, to figure and landscape painting.
-

Kim Whanki
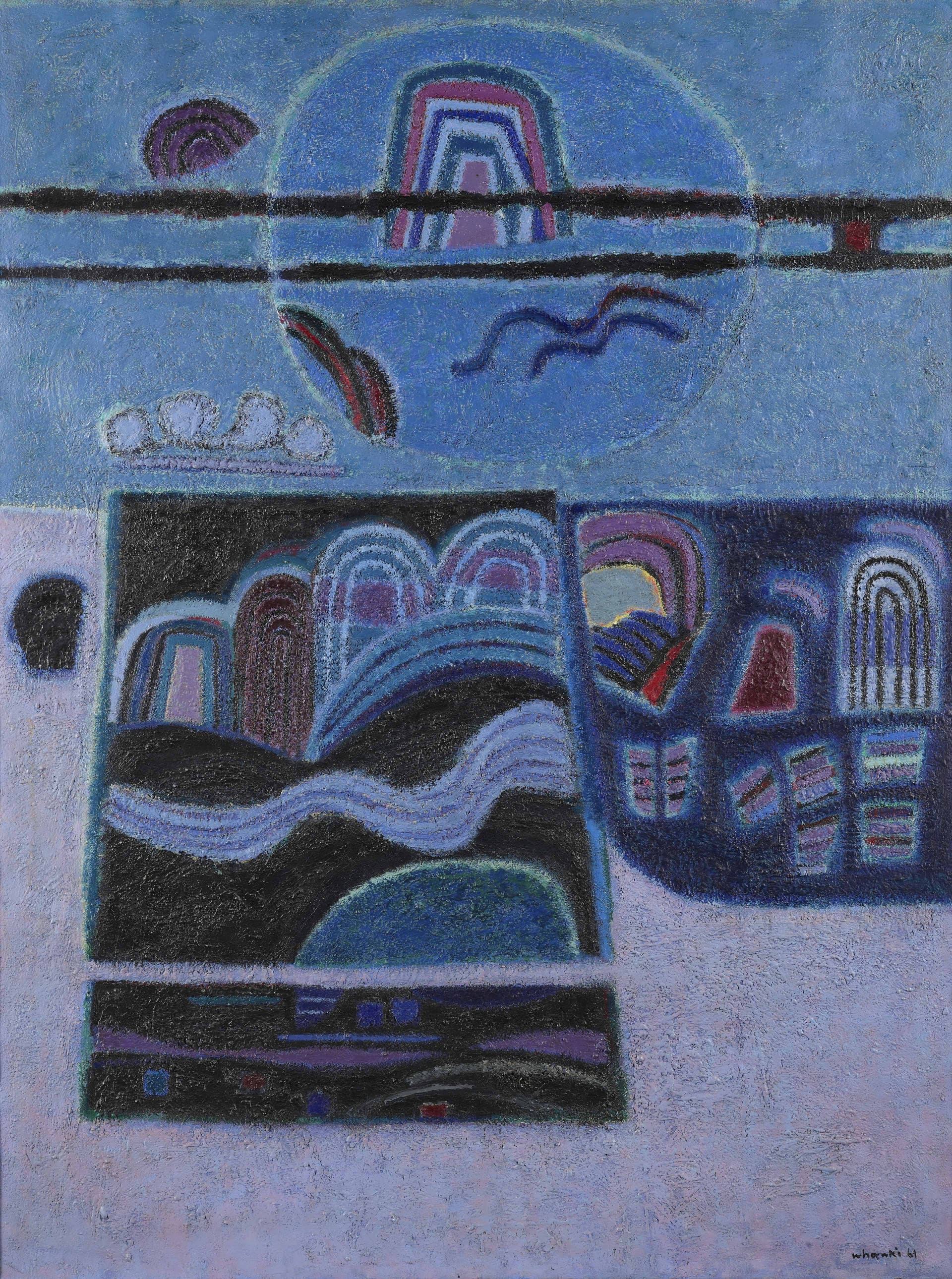
Kim Whanki (1913-1974, pen name Suhwa) was born in Sinan, Jeollanamdo, and his family origin was from Gimhae. He studied at the Department of Fine Arts at Nihon University, Tokyo, Japan from 1933 to 1936. He joined the Avant-Garde Western Art Institute in 1934 and submitted his work to Avant-Garde art associations, such as the Second Division Exhibition Nikaten (Nika Art Exhibition) and the Exhibition of the Free Artists Association (Jiyu Bijutsuka Kyokai). After independence, he organized the New Realism Group and worked as a professor in the Department of Fine Art at Seoul National University (1946-1950) and Hongik University (1952-55). He lived in Paris from 1956 to 1959, and after his return, he became a professor and later the Dean of the Fine Art College at Hongik University (1959-1963). He participated in the seventh Sao Paulo Biennale and won an honorary award, and then moved to New York. He abruptly passed away while having a solo exhibition at Poindexter Gallery, New York, ironically when his career in the US was at its peak. As a pioneer of Korean abstract art, he started by working in geometric abstraction and moved on to semi-abstract work that featured natural motifs such as the mountain, the moon, and the river. After moving to the U.S., he returned to abstraction with his so-called "dot paintings." His painting 16-Ⅳ-70 #166 Where, in What Form, Shall We Meet Again? (1970), was awarded a grand prize at the Korean Art Grand Award Exhibition and has inspired many contemporary Korean artists. His work Rondo (1938) was selected as No. 535 within the national Registered Cultural Properties.